Introduction
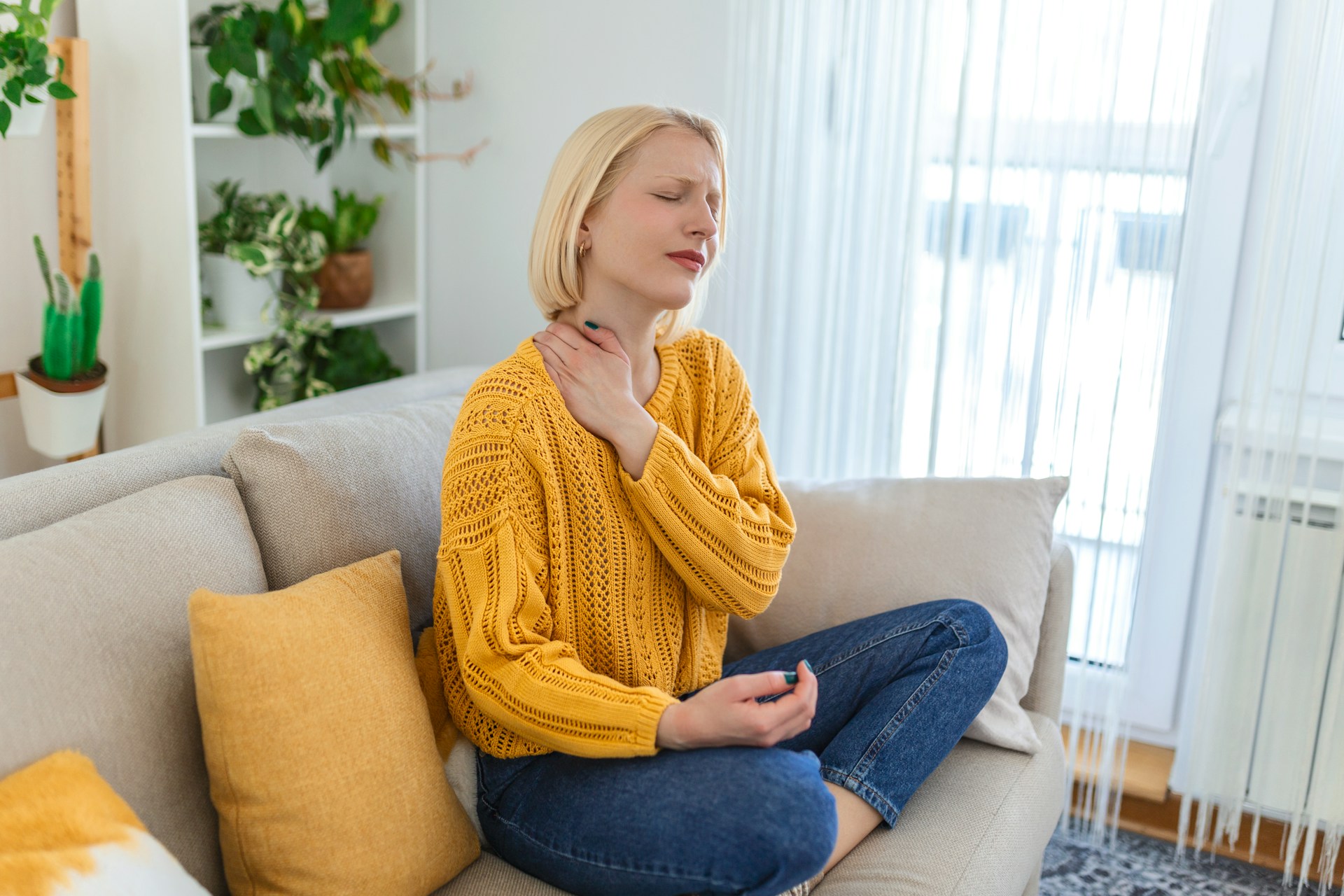
Sciatica is a common condition characterized by pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back through the hips and buttocks and down each leg. It usually affects only one side of the body. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for sciatica can help those affected manage their condition and find relief.
Symptoms of Sciatica
Sciatica symptoms can vary widely but typically include:
- Radiating Pain: A sharp, burning, or shooting pain that starts in the lower back and travels down the buttock and the back of the leg.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations of pins and needles, often in the leg or foot.
- Muscle Weakness: Weakness in the affected leg, which can affect mobility and stability.
- Lower Back Pain: Sometimes, pain in the lower back accompanies the leg pain, though the leg pain is usually more severe.
- Pain that Worsens with Movement: Activities such as sitting, standing for long periods, or sudden movements can exacerbate the pain.
Causes of Sciatica
Several conditions can lead to sciatica by compressing or irritating the sciatic nerve, including:
- Herniated Disc: When a disc in the lower spine ruptures or bulges, it can press on the sciatic nerve.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal in the lower back can compress the sciatic nerve.
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Age-related changes in the spine can lead to disc degeneration, which may cause sciatica.
- Spondylolisthesis: A condition where one vertebra slips over another, potentially compressing the nerve.
- Piriformis Syndrome: The piriformis muscle, located in the buttocks, can irritate the sciatic nerve if it spasms or becomes tight.
- Injury or Trauma: Accidents or injuries that affect the lower back or pelvis can lead to sciatica.
- Tumors: Though rare, tumors in the spine or pelvis can press on the sciatic nerve.
- Infections: Infections in the spine can also cause sciatica.
Treatment Options for Sciatica
The treatment for sciatica depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. Common treatment options include:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms and engaging in gentle movements to prevent stiffness.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants can help manage pain and inflammation.
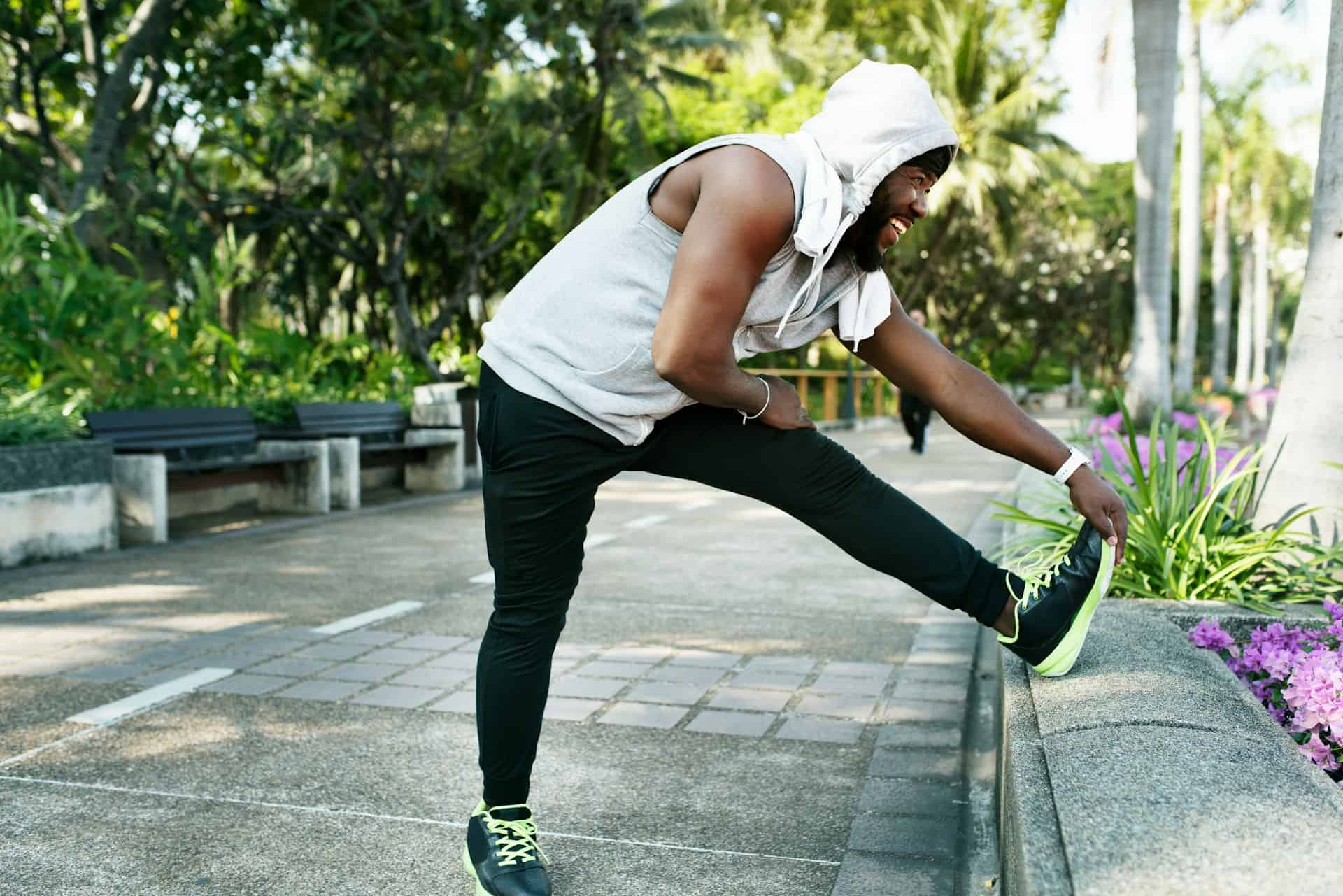
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches designed to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve flexibility. Physical therapists can also teach proper posture and movement techniques to reduce strain on the sciatic nerve.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or ice packs to the affected area can reduce pain and inflammation.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as chiropractic adjustments, massage, and acupuncture can provide relief for some individuals.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief by targeting the affected area.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the sciatic nerve. Surgical options include discectomy, laminectomy, and spinal fusion.
Prevention Tips
Preventing sciatica involves adopting healthy habits and maintaining good posture, such as:
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in activities that strengthen the core and back muscles and improve flexibility.
- Maintain Good Posture: Ensure proper alignment of the spine while sitting, standing, and lifting.
- Lift Properly: Use your legs to lift heavy objects and avoid twisting your back.
- Ergonomic Workstation: Set up your workstation to promote good posture and reduce strain on the lower back.
- Stay Active: Avoid prolonged periods of inactivity, which can weaken the muscles supporting the spine.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put additional strain on the lower back and sciatic nerve.
Conclusion
Sciatica can significantly impact daily life due to its painful and debilitating symptoms. By understanding its causes and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and alleviate their discomfort. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.