Introduction
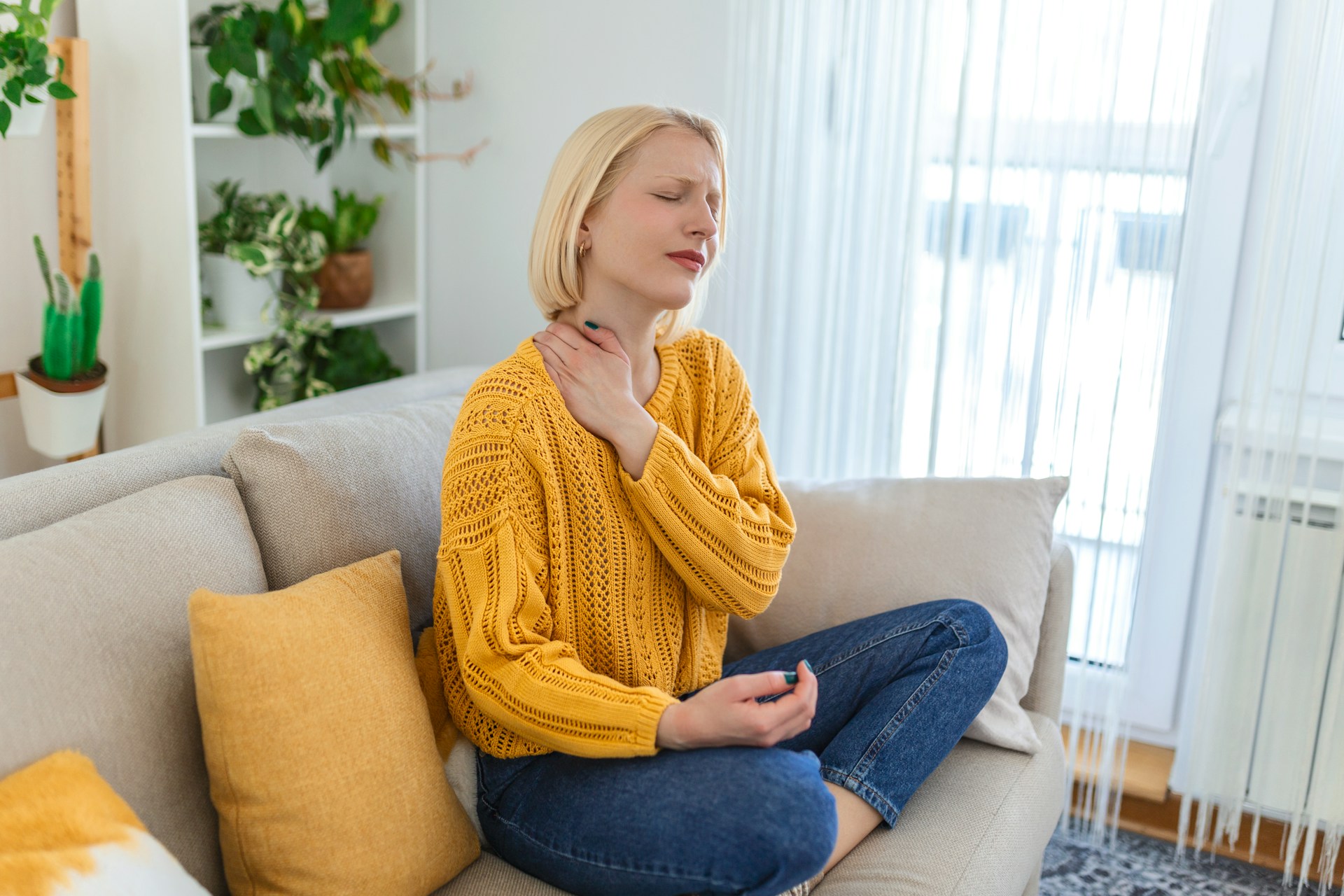
Postural tension, often resulting from prolonged periods of poor posture, can lead to various musculoskeletal issues. This condition is increasingly common due to modern lifestyles that involve long hours of sitting and extensive use of electronic devices. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for postural tension is essential for effectively managing and preventing this condition.
Symptoms of Postural Tension
Postural tension can manifest in various ways, depending on the severity and duration of poor posture. Common symptoms include:
- Muscle Pain and Tightness: Persistent ache or tightness in the neck, shoulders, and back muscles.
- Headaches: Tension headaches caused by strain in the neck and shoulder muscles.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the neck, shoulders, and back due to muscle stiffness.
- Fatigue: General tiredness and fatigue, often due to muscle strain and poor blood circulation.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Limited ability to move the head, neck, and shoulders freely.
- Numbness and Tingling: Sensations of pins and needles, often in the arms and hands, due to nerve compression.
- Postural Deformities: Development of rounded shoulders, forward head posture, and an exaggerated curve in the lower back.
Causes of Postural Tension
Several factors can contribute to postural tension, including:
- Prolonged Sitting: Spending long hours sitting, especially with poor ergonomics, can strain muscles and lead to tension.
- Poor Posture: Slouching, hunching over a desk, and using electronic devices with poor posture can contribute to muscle tension.
- Repetitive Movements: Repeated movements or maintaining the same position for extended periods can strain muscles.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyle can weaken muscles, making them more susceptible to tension and strain.
- Stress: Emotional stress can cause muscle tightening and contribute to postural tension.
- Inadequate Workstation Ergonomics: Poorly designed workspaces that do not support proper posture can lead to muscle strain.
Treatment Options for Postural Tension
Treating postural tension involves a combination of lifestyle changes, physical therapies, and ergonomic adjustments. Common treatment options include:
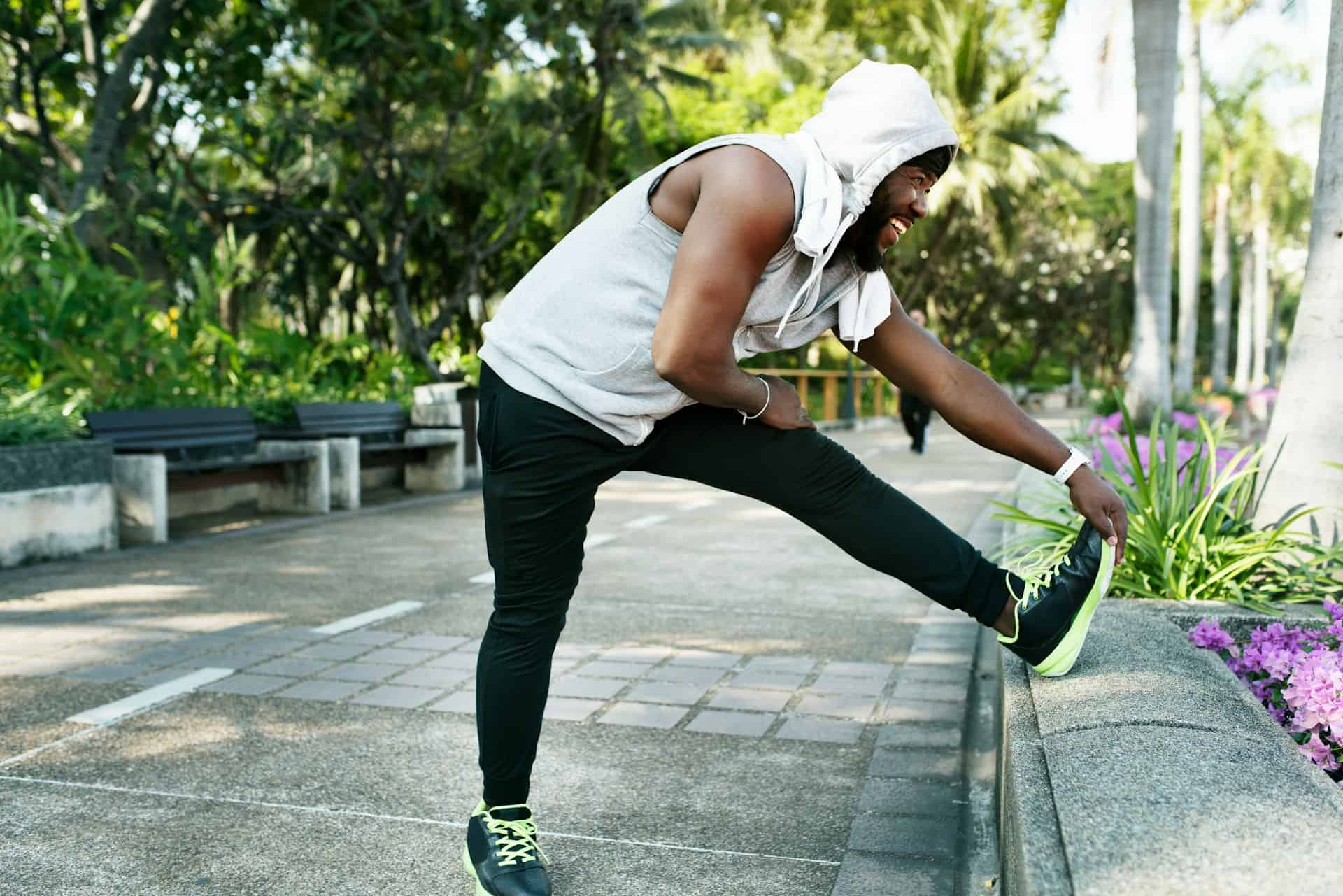
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches designed to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and correct posture.
- Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can help relieve muscle tension and improve blood circulation.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments can help correct spinal misalignments and reduce muscle tension.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Modifying your workstation to promote good posture, including adjusting chair height, desk setup, and monitor placement.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat to relax muscles and improve blood flow, or using cold packs to reduce inflammation and numb pain.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers and muscle relaxants can help manage pain and reduce muscle tension.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and muscle tension.
Prevention Tips
Preventing postural tension involves adopting healthy habits and maintaining good posture throughout daily activities. Tips for prevention include:
- Maintain Good Posture: Keep your back straight, shoulders back, and head aligned with your spine while sitting and standing.
- Take Regular Breaks: Stand up, stretch, and move around every 30 minutes to prevent muscle strain from prolonged sitting.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in activities that strengthen your core and back muscles, such as swimming, yoga, and Pilates.
- Ergonomic Workstation: Set up your workstation to support proper posture, including using an adjustable chair, desk, and monitor.
- Stay Active: Incorporate physical activity into your daily routine to keep muscles strong and flexible.
- Practice Stress Management: Use stress-relief techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises to reduce muscle tension.
- Use Proper Lifting Techniques: Bend your knees and keep your back straight when lifting objects to avoid straining your back muscles.
Conclusion
Postural tension is a common issue that can significantly impact daily life. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and alleviate their discomfort. If you experience persistent or severe postural tension, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.